Vegetable oils are fatty substances and are essentially composed of saturated or unsaturated fatty acids with omega 3, omega 6 or omega 9. This composition gives them very useful properties in cosmetics, aromatherapy and food. To understand how an oil works and especially whether it is good for us or not, you must already know what it is made of. La Compagnie des Sens has given you a short summary of the main constituents of a vegetable oil.
Introduction to the biochemical composition of vegetable oils
We qualify vegetable oil, an oil obtained by cold pressing or extraction, but also an oily macerate which results from the maceration of a plant in a vegetable oil. Being a fat body, vegetable oil is not not miscible in water nor in alcohol, that is to say it will not dissolve in it. Depending on the temperature at which the oil is liquid, we can speak ofoil or butter : for example, theArgan produces a liquid oil at room temperature, while the Shea is found in the form of butter at the same temperature.
Fatty acid composition of vegetable oils
Fatty acids are molecules that represent a source of energy for humans. Mostly provided by food, fatty acids can also be synthesized by our body. However, some cannot be synthesized and must be supplied through the diet; these fatty acids are called essential. Together, fatty acids form lipids.
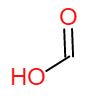
A fatty acid is made up of a chain of carbon and hydrogen atoms, with a COOH carboxylic acid function at one end. This forms a more or less long chain depending on the type of fatty acid. Depending on the number of hydrogen atoms found on these carbons, we distinguish several configurations of fatty acids: the unsaturated and the saturated.
Opposite: COOH carboxylic acid function
Unsaturated fatty acids
Unsaturated fatty acids are composed of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds (C=C), allowing them to be classified into two categories:
Saturated fatty acids
Unlike unsaturated fatty acids, saturated fatty acids only have single carbon bonds, that is, all carbons are connected to hydrogen atoms. Saturated fatty acids are generally present in solid form at room temperature, an oil composed mainly of saturated fatty acids can therefore have a solid appearance like Coconut or Shea Butter. When dosed appropriately, in a healthy and balanced diet, saturated fatty acids can be very good sources of energy and vitamins.
Here are some examples of vegetable oils classified according to their fatty acid composition:
-
Rich in saturated fatty acids: the oil of Coco, of Monoi or even the Shea Butter
-
Rich in omega 3: the oil of Chia, of Perilla, of Sea buckthorn seeds orInca Inchi
-
Rich in omega 6: the oil of Blackberry, of Nigella, d’Evening primrose or Pumpkin seeds
-
Rich in omega 9: the oil of Camellia, d’Almond, of St. John's wort or Karanja
Other components of vegetable oils, unsaponifiables
Although vegetable oils are largely composed of fatty acids, it is important to note that there are other compounds such as unsaponifiable. It is a kind of residue insoluble in water, called non-glyceridic part, and which is obtained by saponification of oil. Saponification is the process of transforming an oil into soap by adding soda. The nature of these unsaponifiables varies depending on the vegetable oil used, the main categories of unsaponifiables are carotenoids (vitamin A precursors), tocopherols (powerful anti-oxidants) and sterols (excellent for skin elasticity). Even if they are in very small quantities in vegetable oil, often less than 1%, their actions nevertheless remain very effective.
Among these unsaponifiables the category of vitamins is very interesting, we will find for example:
- There vitamin A which is a powerful antioxidant, which preserves the skin and protects the body from infections. When ingested, it can also help facilitate bone growth and promote good vision.. Precursors are found in the oil of Carrot, but also in the oil of Jojoba.
- There vitamin B in its generality contributes to the production of energy by the body. Each subcategory of vitamin B (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B8, B9 and B12) has slightly more specific properties. For example, vitamin B is found in the oil of Wheat germ and theoil of Sesame.
- There vitamin C is also a powerful antioxidant which contributes to good bone health. It also helps accelerate healing. Vitamin C is found in the oil of Rosehip and D'Lawyer.
- There vitamin D is quite well known, since it is what is secreted during exposure to the sun. It is useful for the proper functioning of the immune system and the good health of bones and teeth. We find it in the oil ofAlmond and of Borage.
- There vitamin E is one of the most antioxidant vitamins. Anti-inflammatory, it also contributes to the proper functioning of the cardiovascular system. It is found in the oil of Hazelnut and other nuts, but also in the oil of Hemp.
- There vitamin K is useful for clotting blood and hardening soft tissues. We find it in the oil of Safflower but also in that of Broccoli.
All these vitamins can be present in vegetable oils and provide their properties to act at the heart of your body, whether they are used on the skin or ingestion depending on the desired effect.
Was this article helpful to you?
Average grade: 4.2 ( 96 votes)
Bibliography
Work : de la Charie, T. (2019). Treat yourself with essential oils. Why and how does it work? Editions du Rocher.
Work : Pobeda, M. (2011). The benefits of vegetable oils, learn to know them and use them, for health and beauty. Editions Hachettes Livres (Marabout).
Website : The health effects of unsaturated fatty acids - summary, by Joanne Lunn and Hannah E. Theobald, nutritionists, for the British Nutrition Foundation. (2006) http://www.eufic.org/article/fr/rid/health-effects-unsaturated-fatty-acids-Summary/
Website : Unsaponifiables, or how to save our skin from the ravages of time, by Missrimel, published March 31, 2011. http://www.soapacadabra.fr/archives/2011/03/31/20768119.html
Website : What is the difference between omega 3 and omega 6? Updated 08/20/2015. http://www.allodocteurs.fr/alimentation/nutriments/omega-3-6/quelle-est-la-difference-entre-omega-3-et-omega-6_16504.html
Website : Cardiovascular diseases: saturated fats not so risky? Florian Gouthière for allodocteurs.fr. Updated 05/31/2014. http://www.allodocteurs.fr/actualite-sante-entreprises-cardiovascular-des-graisses-saturees-pas-si-riskes-_12898.html



